Firebase App Check Configuration for roar-firekit and roar-dashboard
Overview
This document outlines the steps taken to configure App Check for secure access to Firebase services through the roar-dashboard Vue application, which uses the roar-firekit TypeScript package to manage Firebase services.
What is Firebase App Check?
Firebase App Check is a security feature designed to protect your Firebase resources from unauthorized access by verifying that incoming traffic originates from your app. It helps safeguard against abuse and ensures that only legitimate requests from your app can access your Firebase services, such as Firestore, Realtime Database, Cloud Functions, and Storage.
How Does Firebase App Check Work?
App Check works by generating an App Check token on the client side and sending it along with requests to your Firebase backend services. The Firebase backend then verifies this token to ensure that the request is coming from an authenticated and authorized client app.
Enabling Firebase App Check
To use Firebase App Check, it must be enabled in the Firebase Console for each service you want to protect. You'll also need to integrate the App Check SDK into your app and configure it with an appropriate provider, such as reCAPTCHA for web apps or DeviceCheck/SafetyNet for mobile apps.
The App Check web console can be found here.
Monitored vs. Enforced Mode
Once App Check is enabled, your project can operate in one of two states:
Monitored Mode: In this state, App Check is enabled, and requests without valid App Check tokens are allowed but logged. This mode is useful for gradually introducing App Check into your app, as it allows you to monitor traffic and identify any potential issues without disrupting service to legitimate users.
Enforced Mode: In this state, Firebase services strictly require valid App Check tokens for every request. Requests without a valid token are rejected. This mode offers the highest level of security by ensuring that only authenticated requests from your app can access your Firebase resources.
Firebase App Check is a crucial tool for enhancing the security of your Firebase projects. By enabling it and moving from Monitored to Enforced mode, you can protect your app and its users from unauthorized access and abuse, ensuring that only legitimate requests are processed by your Firebase services.
Generating a Debug Token for Local Development
When developing in a local environment, you can use a debug token to bypass App Check verification. This allows you to test your app without having to pass the App Check verification step. The debug token is a private key that should not be exposed or shared publicly.
Steps to Generate and Register a Debug Token
Generate the Debug Token:
- Pull the main branch and run the development server:
npm run dev - Open the developer console, and you will see a message that includes a new debug token.

- Pull the main branch and run the development server:
Save the Debug Token:
- Save the generated debug token in your
.envfile:VITE_APPCHECK_DEBUG_TOKEN=the-generated-token-from-developer-console
- Save the generated debug token in your
Register the Debug Token:
- This token IS NOT valid until it is registered on the Firebase web console.
- Register the token on the Firebase App Check console for BOTH DEVELOPMENT PROJECTS:
- Click the three-dots menu on the right side of the screen and select "Manage debug tokens".
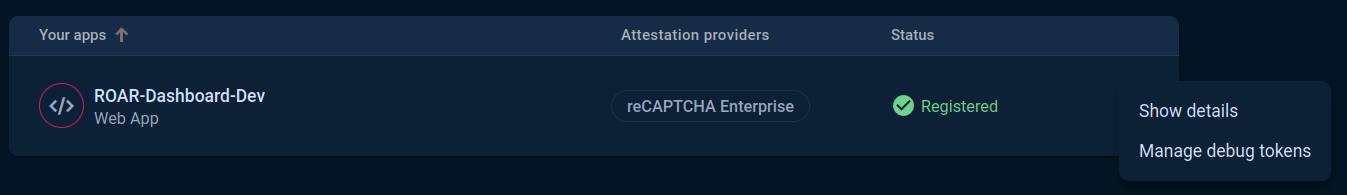
- Within the modal, click "Add debug token".
- Name the token using the following pattern and copy-paste the generated debug token into the field, then click "Done" to save the changes:
app-check-debug-token-{your-firstname}-{your-lastname}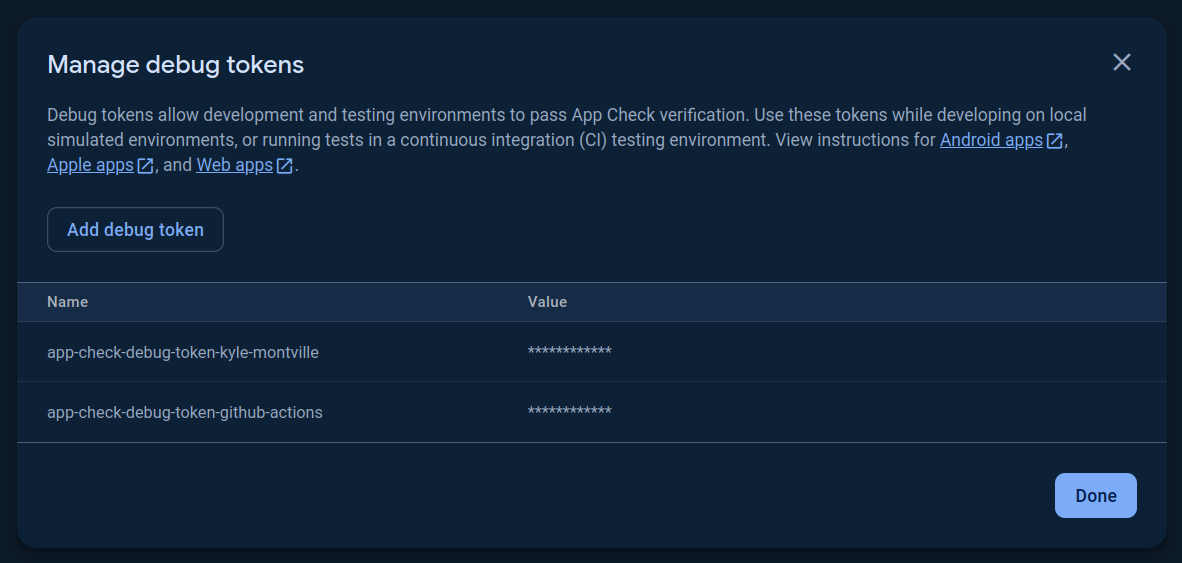
Verify Local Development Setup:
- You should now be set up to run code on
localhostwithout needing App Check verification. - Requests made without a valid debug token will fail with the error message attached.
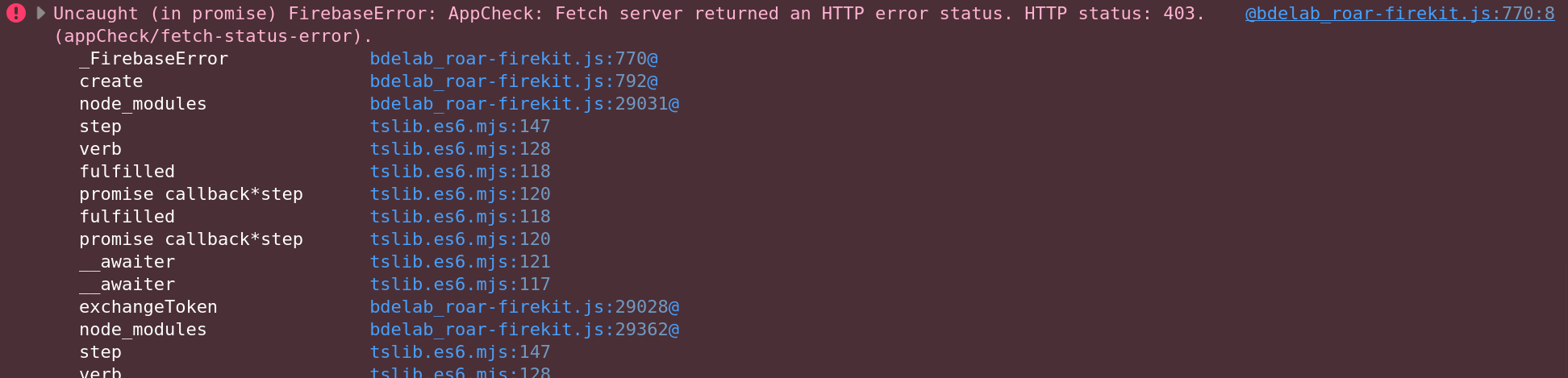
- You should now be set up to run code on
Environment Setup
Environment Variables
Environment variables are set up in the roar-dashboard project to configure App Check tokens that are used by roar-firekit. These variables are managed using .env files in the roar-dashboard project and are prefixed according to Vite's requirements.
- Vite Configuration: Since
roar-dashboardis bundled with Vite, environment variables are prefixed withVITE_and accessed usingimport.meta.env.
Example .env File in roar-dashboard
VITE_APPCHECK_DEBUG_TOKEN=your_debug_token_value
VITE_APPCHECK_SITE_KEY=your_site_key_value
Accessing Environment Variables in roar-dashboard
In the roar-dashboard Vue app, environment variables are accessed and passed to roar-firekit when initializing Firebase services:
appConfig = {
apiKey: 'AIzaSyDw0TnTXbvRyoVo5_oa_muhXk9q7783k_g',
authDomain: isStaging ? 'roar-staging.web.app' : 'roar.education',
projectId: 'gse-roar-assessment',
storageBucket: 'gse-roar-assessment.appspot.com',
messagingSenderId: '757277423033',
appId: '1:757277423033:web:d6e204ee2dd1047cb77268',
siteKey: import.meta.env.VITE_GSE_ROAR_ASSESSMENT_APPCHECK_SITE_KEY,
debugToken: import.meta.env.VITE_APPCHECK_DEBUG_TOKEN,
};
adminConfig = {
apiKey: 'AIzaSyBz0CTdyfgNXr7VJqcYOPlG609XDs97Tn8',
authDomain: isStaging ? 'roar-staging.web.app' : 'roar.education',
projectId: 'gse-roar-admin',
storageBucket: 'gse-roar-admin.appspot.com',
messagingSenderId: '1062489366521',
appId: '1:1062489366521:web:d0b8b5371a67332d1d2728',
measurementId: 'G-YYE3YN0S99',
siteKey: import.meta.env.VITE_GSE_ROAR_ADMIN_APPCHECK_SITE_KEY,
debugToken: import.meta.env.VITE_APPCHECK_DEBUG_TOKEN,
};
App Check Initialization in roar-firekit
roar-firekit initializes Firebase and App Check based on the configuration provided by roar-dashboard. App Check tokens are passed as part of the configuration to ensure secure access to Firebase services.
Initialization of App Check
In roar-firekit, the App Check is initialized using the provided siteKey and debugToken:
export const initializeAppCheckWithRecaptcha = (
app: FirebaseApp,
name: string,
siteKey: string,
debugToken: string,
) => {
const hostname = window.location.hostname;
const regex = /^https:\/\/roar-staging--pr.*-.*\.web\.app$/;
// Use the DEBUG reCAPTCHA key for local development and PR deployments
// This allows us to bypass the reCAPTCHA domain verification
// Debug token is a private key passed in from a .env file and should not be exposed
if (hostname === 'localhost' || regex.test(window.location.href)) {
try {
(self as any).FIREBASE_APPCHECK_DEBUG_TOKEN = debugToken;
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Error setting App Check debug token: ${error}`);
}
}
try {
console.log(`Initializing App Check with reCAPTCHA provider for project "${name}" with site key ${siteKey}`);
return initializeAppCheck(app, {
provider: new ReCaptchaEnterpriseProvider(siteKey as string),
isTokenAutoRefreshEnabled: true,
});
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Error initializing App Check with reCAPTCHA provider: ${error}`);
}
};
Initialization of Firebase with App Check
In roar-firekit, Firebase is initialized with the App Check initialization function from above. The App Check token is then retrieved and passed to the roar-dashboard as appCheckToken for secure access to Firebase services:
export const initializeAppCheckWithRecaptcha = (
app: FirebaseApp,
name: string,
siteKey: string,
debugToken: string,
) => {
const hostname = window.location.hostname;
const regex = /^https:\/\/roar-staging--pr.*-.*\.web\.app$/;
// Use the DEBUG reCAPTCHA key for local development and PR deployments
// This allows us to bypass the reCAPTCHA domain verification
// Debug token is a private key passed in from a .env file and should not be exposed
if (hostname === 'localhost' || regex.test(window.location.href)) {
try {
(self as any).FIREBASE_APPCHECK_DEBUG_TOKEN = debugToken;
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Error setting App Check debug token: ${error}`);
}
}
try {
console.log(`Initializing App Check with reCAPTCHA provider for project "${name}" with site key ${siteKey}`);
return initializeAppCheck(app, {
provider: new ReCaptchaEnterpriseProvider(siteKey as string),
isTokenAutoRefreshEnabled: true,
});
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Error initializing App Check with reCAPTCHA provider: ${error}`);
}
};
export enum AuthPersistence {
local = 'local',
session = 'session',
none = 'none',
}
export interface MarkRawConfig {
auth?: boolean;
db?: boolean;
functions?: boolean;
}
type FirebaseProduct = Auth | Firestore | Functions | FirebaseStorage;
export const initializeFirebaseProject = async (
config: FirebaseConfig,
name: string,
authPersistence = AuthPersistence.session,
markRawConfig: MarkRawConfig = {},
// App Check reCAPTCHA site keys and debug token
siteKey = '',
debugToken = '',
) => {
const optionallyMarkRaw = <T extends FirebaseProduct>(productKey: string, productInstance: T): T => {
if (_get(markRawConfig, productKey)) {
return markRaw(productInstance);
} else {
return productInstance;
}
};
if ((config as EmulatorFirebaseConfig).emulatorPorts) {
const app = initializeApp({ projectId: config.projectId, apiKey: config.apiKey }, name);
const ports = (config as EmulatorFirebaseConfig).emulatorPorts;
const auth = optionallyMarkRaw('auth', getAuth(app));
const db = optionallyMarkRaw('db', getFirestore(app));
const functions = optionallyMarkRaw('functions', getFunctions(app));
const storage = optionallyMarkRaw('storage', getStorage(app));
connectFirestoreEmulator(db, '127.0.0.1', ports.db);
connectFunctionsEmulator(functions, '127.0.0.1', ports.functions);
const originalInfo = console.info;
// eslint-disable-next-line @typescript-eslint/no-empty-function
console.info = () => {};
connectAuthEmulator(auth, `http://127.0.0.1:${ports.auth}`);
console.info = originalInfo;
return {
firebaseApp: app,
auth,
db,
functions,
storage,
};
} else {
const app = safeInitializeApp(config as LiveFirebaseConfig, name);
// Initialize App Check with reCAPTCHA provider before calling any other Firebase services
// Grab the App Check token for use in the ROAR Dashboard Axios Calls to Firebase
const appCheck = initializeAppCheckWithRecaptcha(app, name, siteKey, debugToken);
const appCheckToken = await getToken(appCheck);
const auth = optionallyMarkRaw('auth', getAuth(app));
const db = optionallyMarkRaw('db', getFirestore(app));
const functions = optionallyMarkRaw('functions', getFunctions(app));
const storage = optionallyMarkRaw('storage', getStorage(app));
let performance: FirebasePerformance | undefined = undefined;
try {
performance = getPerformance(app);
// eslint-disable-next-line @typescript-eslint/no-explicit-any
} catch (error: any) {
if (error.code !== 'performance/FB not default') {
throw error;
}
}
const kit = {
firebaseApp: app,
appCheckToken: appCheckToken.token,
auth: auth,
db: db,
functions: functions,
storage: storage,
perf: performance,
};
// Auth state persistence is set with ``setPersistence`` and specifies how a
// user session is persisted on a device. We choose in session persistence by
// default because many students will access the ROAR on shared devices in the
// classroom.
if (authPersistence === AuthPersistence.session) {
await setPersistence(kit.auth, browserSessionPersistence);
} else if (authPersistence === AuthPersistence.local) {
await setPersistence(kit.auth, browserLocalPersistence);
} else if (authPersistence === AuthPersistence.none) {
await setPersistence(kit.auth, inMemoryPersistence);
}
return kit;
}
};
Manually Appending App Check Token to Axios Requests
Since roar-dashboard uses Axios to make requests to Firebase's REST API, the App Check token must be manually appended to each request. The App Check token is retrieved from the Roar Firekit config and passed to Axios as a header.
export const getAxiosInstance = (db = 'admin', unauthenticated = false) => {
const authStore = useAuthStore();
const { roarfirekit } = storeToRefs(authStore);
const axiosOptions = _get(roarfirekit.value.restConfig, db) ?? {};
// Add appCheckToken to the headers if it exists in the firekit config
const appCheckToken = roarfirekit.value[db]?.appCheckToken;
if (appCheckToken) {
axiosOptions.headers = {
...axiosOptions.headers,
'X-Firebase-AppCheck': appCheckToken,
};
}
if (unauthenticated) {
delete axiosOptions.headers;
}
return axios.create(axiosOptions);
};
Summary
- App Check Token Retrieval: The getAppCheckToken() function in roar-firekit retrieves the current App Check token, ensuring that requests are secure.
- Header Injection: The token is appended to the x-firebase-appcheck header in each Axios request to ensure it is validated by Firebase.
The integration between roar-dashboard and roar-firekit ensures secure access to Firebase services using App Check. Environment variables are managed using Vite's import.meta.env, and the App Check token is manually appended to Axios requests to authenticate interactions with Firebase's REST API. This setup allows for both secure and flexible handling of Firebase services across different environments.